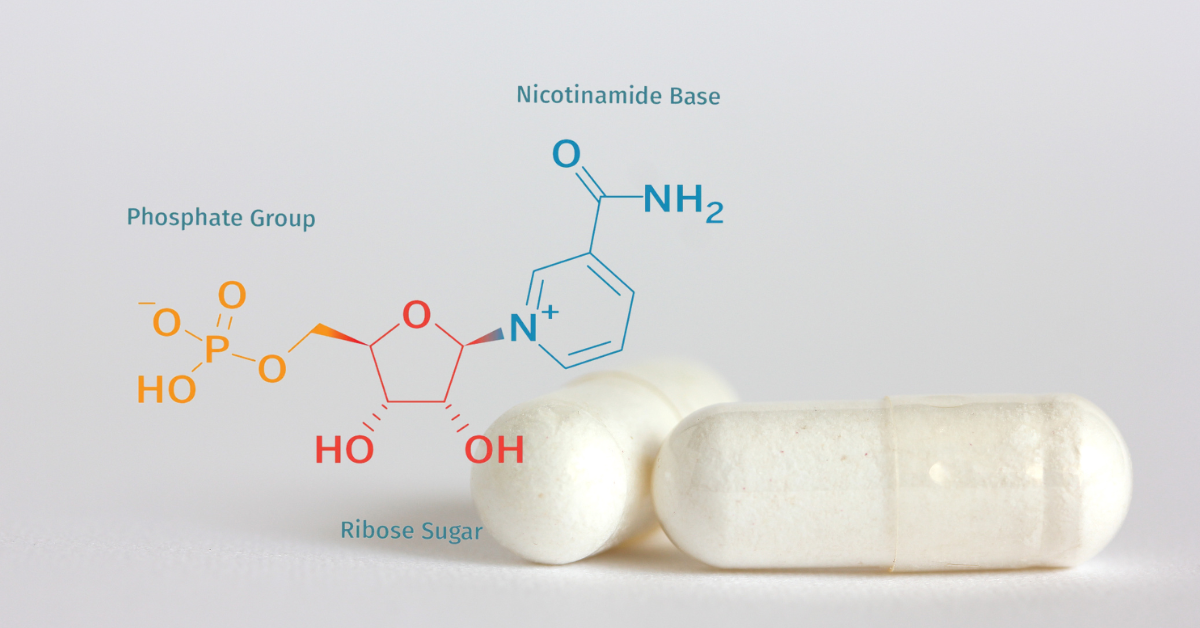
Understanding NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) and Its Role in Health and Aging
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its potential role in cellular metabolism, energy production, and aging processes. NMN is a precursor molecule for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a crucial coenzyme involved in various cellular processes. This article delves deeper into the science behind NMN, its potential health benefits, and the current state of research.
The Science of NMN and NAD+
NAD+ is essential for cellular energy metabolism, DNA repair, and gene expression regulation. As we age, levels of NAD+ decline, which is associated with impaired cellular function and increased susceptibility to age-related diseases. NMN is a key precursor in the biosynthesis of NAD+. When NMN is administered orally, it is rapidly absorbed and converted into NAD+ in cells, potentially restoring cellular NAD+ levels.
Potential Health Benefits of NMN
- Anti-Aging Properties: Research suggests that NMN supplementation can mitigate some aspects of aging by restoring cellular NAD+ levels. Studies in animal models have shown that NMN supplementation can improve mitochondrial function, enhance metabolism, and extend lifespan.
- Metabolic Health: NMN has demonstrated benefits for metabolic health. It may improve insulin sensitivity, reduce fat accumulation, and support healthy blood sugar levels, potentially offering a therapeutic approach for metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Health: NMN supplementation has been linked to improved cardiovascular function in animal studies. It may promote blood vessel health, enhance blood flow, and protect against age-related vascular dysfunction.
- Neuroprotection: NAD+ is crucial for neuronal function and brain health. Some studies suggest that NMN supplementation could support cognitive function and protect against neurodegenerative diseases by enhancing NAD+ levels and mitochondrial function in the brain.
Current Research and Clinical Trials
While much of the evidence supporting NMN’s benefits comes from animal studies, human trials are underway to evaluate its safety, efficacy, and potential applications in humans. These trials aim to determine optimal dosages, assess bioavailability, and investigate specific health outcomes associated with NMN supplementation.
Safety Considerations and Future Directions
Although NMN appears promising, safety considerations and long-term effects in humans are still being investigated. It’s essential for individuals considering NMN supplementation to consult with healthcare professionals, especially if they have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking medications.
In conclusion, NMN represents a fascinating area of research with potential implications for aging-related health issues. While further studies are needed to fully elucidate its mechanisms and benefits, NMN holds promise as a novel therapeutic approach to promote healthy aging and combat age-related diseases.